Puerto rico time zone map: Puerto Rico Time Zone
| Alabama(AL) | Central Standard Time (CST) |
| Alaska(AK) | Alaska Standard Time (AKST) |
| Aleutian Islands Hawaii-Aleutian Standard Time (HST) | |
| Arizona(AZ) | Mountain Standard Time (MST) |
| The Navajo Nation uses Daylight Saving Time (DST), the rest of the state does not | |
| American Samoa | Samoa Time (SST) |
| American Samoa does not use Daylight Saving Time (DST) | |
| Arkansas(AR) | Central Standard Time (CST) |
| California(CA) | Pacific Standard Time (PST) |
| Colorado(CO) | Mountain Standard Time (MST) |
| Connecticut(CT) | Eastern Standard Time (EST) |
| Delaware(DE) | Eastern Standard Time (EST) |
| District of Columbia(DC) | Eastern Standard Time (EST) |
| Florida(FL) | Most of the state: Eastern Standard Time (EST) |
| West of the Apalachicola River: Central Standard Time (CST) | |
| Georgia(GA) | Eastern Standard Time (EST) |
| Guam (GU) | Chamorro Standard Time (ChST) |
| Guam does not use Daylight Saving Time (DST) | |
| Hawaii(HI) | Hawaii-Aleutian Standard Time (HST) |
| Hawaii does not use Daylight Saving Time (DST) | |
| Idaho(ID) | Most of the state: Mountain Standard Time (MST) |
| North of the Salmon River: Pacific Standard Time (PST) | |
| Illinois(IL) | Central Standard Time (CST) |
| Indiana(IN) | Most of the state: Eastern Standard Time (EST) |
| Some counties near the southwestern and northwestern border of the state use Central Standard Time (CST) | |
| Iowa(IA) | Central Standard Time (CST) |
| Kansas(KS) | Most of the state: Central Standard Time (CST) |
| Greeley, Hamilton, Sherman and Wallace counties: Mountain Standard Time (MST) | |
| Kentucky(KY) | Western half of the state: Central Standard Time (CST) |
| Eastern half of the state: Eastern Standard Time (EST) | |
| Louisiana(LA) | Central Standard Time (CST) |
| Maine(ME) | Eastern Standard Time (EST) |
| Maryland(MD) | Eastern Standard Time (EST) |
| Massachusetts(MA) | Eastern Standard Time (EST) |
| Michigan(MI) | Most of the state: Eastern Standard Time (EST) |
| Dickinson, Gogebic, Iron and Menominee Counties: Central Standard Time (CST) | |
| Minnesota(MN) | Central Standard Time (CST) |
| Mississippi(MS) | Central Standard Time (CST) |
| Missouri(MO) | Central Standard Time (CST) |
| Montana(MT) | Mountain Standard Time (MST) |
| Nebraska(NE) | Most of the state: Central Standard Time (CST) |
| Western part of the state: Mountain Standard Time (MST) | |
| Nevada(NV) | Most of the state: Pacific Standard Time (PST) |
| 2 small towns, Jackpot and West Wendover: Mountain Standard Time (MST) | |
| New Hampshire(NH) | Eastern Standard Time (EST) |
| New Jersey(NJ) | Eastern Standard Time (EST) |
| New Mexico(NM) | Mountain Standard Time (MST) |
| New York(NY) | Eastern Standard Time (EST) |
| North Carolina(NC) | Eastern Standard Time (EST) |
| North Dakota(ND) | Most of the state: Central Standard Time (CST) |
| Western North Dakota: Mountain Standard Time (MST) | |
| Northern Mariana Islands(MP) | Chamorro Standard Time (ChST) |
| The CNMI does not use Daylight Saving Time (DST) | |
| Ohio(OH) | Eastern Standard Time (EST) |
| Oklahoma(OK) | Central Standard Time (CST) |
| Oregon(OR) | Most of the state: Pacific Standard Time (PST) |
| Part of Malheur County: Mountain Standard Time (MST) | |
| Pennsylvania(PA) | Eastern Standard Time (EST) |
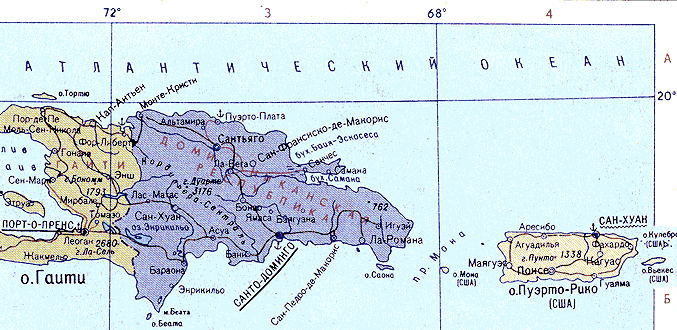
| Puerto Rico (PR) | Atlantic Standard Time (AST) |
| Puerto Rico does not use Daylight Saving Time (DST) | |
| Rhode Island(RI) | Eastern Standard Time (EST) |
| South Carolina(SC) | Eastern Standard Time (EST) |
| South Dakota(SD) | Eastern South Dakota: Central Standard Time (CST) |
| Western South Dakota: Mountain Standard Time (MST) | |
| Tennessee(TN) | West Tennessee: Central Standard Time (CST) |
| Middle Tennessee, plus Marion County: Central Standard Time (CST) | |
| East Tennessee, except Marion County: Eastern Standard Time (EST) | |
| Texas(TX) | Most of the state: Central Standard Time (CST) |
| El Paso and Hudspeth Counties: Mountain Standard Time (MST) | |
| United States Virgin Islands (USVI) | Atlantic Standard Time (AST) |
| The USVI does not use Daylight Saving Time (DST) | |
| Utah(UT) | Mountain Standard Time (MST) |
| Vermont(VT) | Eastern Standard Time (EST) |
| Virginia(VA) | Eastern Standard Time (EST) |
| Washington(WA) | Pacific Standard Time (PST) |
| West Virginia(WV) | Eastern Standard Time (EST) |
| Wisconsin(WI) | Central Standard Time (CST) |
| Wyoming(WY) | Mountain Standard Time (MST) |
World Time Zone Map – GIS Geography
You are free to use our world time zone map for educational and commercial uses. Attribution is required. How to attribute?
Attribution is required. How to attribute?
Time Zones Explained
We have 24 different time zones in the world. Because the Earth rotates 360° every 24 hours, each time zone is 15° longitude apart from the other. (360÷24=15)
The Prime Meridian (Greenwich Meridian) defines the center of the first time zone in the world. This means the Prime Meridian time zone spans from 7.5°W to 7.5°E. Then, the next time to the east spans 7.5°E to 22.5°E.
Gaining and losing time
When you move to the right, you gain time (fast time). In other words, for every time zone that you move towards the right, you add one hour. But when you head toward the left, you lose an hour (slow time).
You can find any time by counting how many degrees longitude it is away from Greenwich. For example, it would be 4 pm at 60°E longitude when it’s noon at the Prime Meridian. Whereas it would be 8 am at 60°W longitude
International Date Line
The International Date Line is a north-south line in the Pacific Ocean where you turn your calendar back or ahead one day. The center of the time zone roughly follows 180° longitude without crossing any landmass.
The center of the time zone roughly follows 180° longitude without crossing any landmass.
When you cross the International Date Line moving toward the east, you turn your calendar back one day. Whereas when you go from the west across the International Date Line, you turn your calendar ahead one day.
Irregular Time Zone Boundaries
No time zone in the world runs a perfect north-south line. Instead, they are jagged and adapt to the political boundaries of countries. Also, there can be “irregular square” time zones similar to islands.
For example, the province of Newfoundland and Labrador contains its own time zone with the same name that is UTC -3:30. But the province mostly observes Atlantic Standard Time (AST). Other examples include Afghanistan, Venezuela, and Australia with unusual time zones.
List of Time Zones and Abbreviations
Time zones can have names to help easily identify them. For example, this United States time zone map shows the six designated time zones including Eastern, Central, Mountain, Pacific, Alaska, and Hawaii-Aleutian time zones.
Here is a list of time zones and abbreviations that are in use today:
| Name | Description | Relative to GMT |
|---|---|---|
| GMT | Greenwich Mean Time | GMT |
| UTC | Universal Coordinated Time | GMT |
| ECT | European Central Time | GMT+1:00 |
| EET | Eastern European Time | GMT+2:00 |
| ART | (Arabic) Egypt Standard Time | GMT+2:00 |
| EAT | Eastern African Time | GMT+3:00 |
| MET | Middle East Time | GMT+3:30 |
| NET | Near East Time | GMT+4:00 |
| PLT | Pakistan Lahore Time | GMT+5:00 |
| IST | India Standard Time | GMT+5:30 |
| BST | Bangladesh Standard Time | GMT+6:00 |
| VST | Vietnam Standard Time | GMT+7:00 |
| CTT | China Taiwan Time | GMT+8:00 |
| JST | Japan Standard Time | GMT+9:00 |
| ACT | Australia Central Time | GMT+9:30 |
| AET | Australia Eastern Time | GMT+10:00 |
| SST | Solomon Standard Time | GMT+11:00 |
| NST | New Zealand Standard Time | GMT+12:00 |
| MIT | Midway Islands Time | GMT-11:00 |
| HST | Hawaii Standard Time | GMT-10:00 |
| AST | Alaska Standard Time | GMT-9:00 |
| PST | Pacific Standard Time | GMT-8:00 |
| PNT | Phoenix Standard Time | GMT-7:00 |
| MST | Mountain Standard Time | GMT-7:00 |
| CST | Central Standard Time | GMT-6:00 |
| EST | Eastern Standard Time | GMT-5:00 |
| IET | Indiana Eastern Standard Time | GMT-5:00 |
| PRT | Puerto Rico and US Virgin Islands Time | GMT-4:00 |
| CNT | Canada Newfoundland Time | GMT-3:30 |
| AGT | Argentina Standard Time | GMT-3:00 |
| BET | Brazil Eastern Time | GMT-3:00 |
| CAT | Central African Time | GMT-1:00 |
Time zones in Russia – table with time difference
Contents
Time zones of Russia, history
In 1884, Russia was not among those states that adopted the division into time zones.
At the World Meridian Conference, which was held in Washington, the astronomer Otto Struve, who represented the country, negatively assessed the project of dividing into time zones.
And in Russia everything remained the same, solar time was decisive. The tsarist government did not dare to change anything in this matter.
However, the revolution of 1917 changed not only the state of Russian society, but also the current time.
A few months after the October coup, the Council of People’s Commissars (Council of People’s Commissars) issued a decree, which approved the zone division – for a uniform time reference with the whole civilized world, which should greatly simplify relations between peoples, registration of events and phenomena in time.
The country was divided into 11 time zones, their borders were drawn almost everywhere along the meridians.
Map of time zones in Russia
detailed map of Russia (clickable image)
From August 31, 2011 to October 25, 2014, there were 9 time zones in the Russian Federation.
In connection with the appeal of President Dmitry Medvedev in his message to the Federal Assembly on reducing the number of time zones to another time (Moscow time), the Samara region was transferred.
The same happened with Udmurtia. Chukotka and Kamchatka switched to Magadan time.
In accordance with the Federal Law “On the calculation of time”, since October 26, 2014, 11 time zones have been operating on the territory of the Russian Federation.
Curious facts about the time zones of Russia
- The Republic of Yakutia (Sakha) lies in three time zones, the Sakhalin region – in two, the rest of the regions and regions of Russia are within the same time zone;
- the territory of the Republic of Tatarstan adheres to Moscow time, and their neighbors in Bashkiria live according to MSK+2 time. The river Ik separates the republics, and the bridges along it are jokingly called the longest;
- Russia’s Ratmanov Island in the Bering Strait is 4 kilometers away from the US-owned Krusenstern Island, no more than 20 minutes by motorboat.
 However, according to the rules, these islands are separated by 21 hours of time.
However, according to the rules, these islands are separated by 21 hours of time.
In what time zones is Russia located
There are officially 11 time zones in Russia.
The country has the largest number of time zones in the surrounding territories, and does not adhere to Daylight Saving Time (DST) without changing the clock back and forth.
- UTC +02:00 Kaliningrad Time Zone (KALT: MSK-1) – includes the western region, which is called the Kaliningrad region.
- UTC +03:00 The Moscow Time Zone (MSK) is the most densely populated, including 48 federal subjects in the European part of Russia. There are well-known tourist places such as Moscow, St. Petersburg and the ancient cities of the Golden Ring.
- UTC +04:00 Samara Time Zone (Samara Time Zone (SAMT): MSK + 1) – covers 4 regions: Samara region, Astrakhan region, Ulyanovsk region, Udmurt Republic.
- UTC +05:00 Yekaterinburg Time Zone (YEKT: MSK+2) – includes 9 federal subjects located to the east of the Ural Mountains.

- UTC +06:00 Omsk Time Zone (OMST: MSK + 3) – the belt includes 1 region of southwestern Siberia: Tomsk region.
- UTC +07:00 Krasnoyarsk Time Zone (KRAT: MSK + 4) – covers 8 regions in southern Siberia: Novosibirsk Region, Tomsk Region, Kemerovo Region, Krasnoyarsk Territory, Altai Territory, Altai Republic, Republic of Khakassia, Republic of Tyva.
- UTC +08:00 The Irkutsk Time Zone (IRKT: MSK+5) includes 2 federal subjects in the southeastern part of Siberia around the famous Lake Baikal.
- UTC +09:00 Yakut time zone (Yakutsk Time Zone (YAKT): MSK + 6) – stretches along the entire Trans-Baikal Territory, the Amur Region and the western part of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia).
- UTC +10:00 Time zone of Vladivostok (Vladivostok Time Zone (VLAT): MSK + 7) – covers 4 regions of the Far East and the central part of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia).
- UTC +11:00 Magadan Time Zone (MAGT: MSK + 8) – covers the western part of Sakha (Yakutia), the Sakhalin region and the targets of the Northern Kuril Islands.

- UTC +12:00 Kamchatka Time Zone (PETT: MSK + 9) – covers the easternmost regions of Russia, which are called Chukotka and the Kamchatka Territory borders on Alaska (USA) and Japan.
Moscow time (MSK) is widely used in broadcast programs and train schedules throughout the country.
That’s why, along with the UTC offset, we also mention the offset from Moscow time for different places in Russia.
UTC (temps Universel Coordonne) is the time standard used throughout the world.
Below is a list of time zones in which major Russian cities are located, including the capital Moscow, administrative centers (in bold), major metropolitan areas, tourist and other places.
Map showing the time zones adopted in each countryWhat is a time zone? Time zone is a concept borrowed from geography, consisting of each of the twenty-four chronometric time regions into which our planet is divided. Simply put, this is the division of the planet Earth into spindles (bands, columns), which allows us to calculate the time in each country of the world by adding or subtracting one hour (1 hour) in accordance with the number of time zones separating us from it. For example, if there are three time zones between country X and country Y, we will have to add or subtract three hours to the time recorded by clocks in one country to determine the exact time in another The system arose because the Earth rotates on its axis from west to east, causing the Sun to illuminate one part while leaving the other in darkness, and a method was needed to standardize time. This is how Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) arose, corresponding to the zero meridian – the meridian of the Royal Observatory in Greenwich (England, Great Britain) This universal time is adopted by convention and is used to determine the rest by adding or subtracting hours depending on whether they are further east or west of this time zone (0), respectively. Time zones are a guide, a landmark for managing time in the world, where we can move quickly across its surface. Every nation on the planet has chosen a time zone to govern, often determined by the one that corresponds to its capital city Some particularly large countries use more than one time zone, such as the USA, Russia, Australia or Canada, because they are crossed by several meridians. In other cases, countries move from one time zone to another depending on the climatic season in which they are in order to make better use of the limited or plentiful daylight hours and thus save electrical energy. hours away from the prime meridian embedyt http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uUpzepELm5s&start=4&width=500&height=280 /embedyt Examples of time zonesBelow is a partial list of time zones and the countries that choose them:
|
|---|
 However, according to the rules, these islands are separated by 21 hours of time.
However, according to the rules, these islands are separated by 21 hours of time.

 Each of these regions is called a time zone or time band and is assigned a specific time zone that applies to the entire population whose geographic location shares the same meridian
Each of these regions is called a time zone or time band and is assigned a specific time zone that applies to the entire population whose geographic location shares the same meridian Similarly, meridian 180° is considered in this system as the international date transition line , i.e. the point at which a day ends and a new one begins
Similarly, meridian 180° is considered in this system as the international date transition line , i.e. the point at which a day ends and a new one begins Howland and Baker Islands (United States of America).
Howland and Baker Islands (United States of America).